 重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
(a) The difference between debt and equity in an entity’s statement of financial position is not easily distinguishable for preparers of financial statements. Some financial instruments may have both features, which can lead to inconsistency of reporting. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) has agreed that greater clarity may be required in its definitions of assets and liabilities for debt instruments. It is thought that defining the nature of liabilities would help the IASB’s thinking on the difference between financial instruments classified as equity and liabilities.
Required:
(i) Discuss the key classification differences between debt and equity under International Financial Reporting Standards.
Note: Examples should be given to illustrate your answer. (9 marks)
(ii) Explain why it is important for entities to understand the impact of the classification of a financial instrument as debt or equity in the financial statements. (5 marks)
(b) The directors of Avco, a public limited company, are reviewing the financial statements of two entities which are acquisition targets, Cavor and Lidan.They have asked for clarification on the treatment of the following financial instruments within the financial statements of the entities.
Cavor has two classes of shares: A and B shares. A shares are Cavor’s ordinary shares and are correctly classed as equity. B shares are not mandatorily redeemable shares but contain a call option allowing Cavor to repurchase them. Dividends are payable on the B shares if, and only if, dividends have been paid on the A ordinary shares. The terms of the B shares are such that dividends are payable at a rate equal to that of the A ordinary shares. Additionally, Cavor has also issued share options which give the counterparty rights to buy a fixed number of its B shares for a fixed amount of $10 million. The contract can be settled only by the issuance of shares for cash by Cavor.
Lidan has in issue two classes of shares: A shares and B shares. A shares are correctly classified as equity. Two million B shares of nominal value of $1 each are in issue. The B shares are redeemable in two years’ time at the option of Lidan. Lidan has a choice as to the method of redemption of the B shares. It may either redeem the B shares for cash at their nominal value or it may issue one million A shares in settlement. A shares are currently valued at $10 per share. The lowest price for Lidan’s A shares since its formation has been $5 per share.
Required:
Discuss whether the above arrangements regarding the B shares of each of Cavor and Lidan should be treated as liabilities or equity in the financial statements of the respective issuing companies. (9 marks)
Professional marks will be awarded in question 4 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
 更多“(a) The difference between debt and equity in an entity’s statement of financial position”相关的问题
更多“(a) The difference between debt and equity in an entity’s statement of financial position”相关的问题
第1题
ne aspect of its business is to provide low-cost homes through the establishment of a separate entity, known as a housing association. Minco purchases land and transfers ownership to the housing association before construction starts. Minco sells rights to occupy the housing units to members of the public but the housing association is the legal owner of the building. The housing association enters into loan agreements with the bank to cover the costs of building the homes. However, Minco negotiates and acts as guarantor for the loan, and bears the risk of increases in the loan’s interest rate above a specified rate. Currently, the housing rights are normally all sold out on the completion of a project.
Minco enters into discussions with a housing contractor regarding the construction of the housing units but the agreement is between the housing association and the contractor. Minco is responsible for any construction costs in excess of the amount stated in the contract and is responsible for paying the maintenance costs for any units not sold. Minco sets up the board of the housing association, which comprises one person representing Minco and two independent board members.
Minco recognises income for the entire project when the land is transferred to the housing association. The income recognised is the difference between the total sales price for the finished housing units and the total estimated costs for construction of the units. Minco argues that the transfer of land represents a sale of goods which fulfils the revenue recognition criteria in IAS 18 Revenue. (7 marks)
(b) Minco often sponsors professional tennis players in an attempt to improve its brand image. At the moment, it has a three-year agreement with a tennis player who is currently ranked in the world’s top ten players. The agreement is that the player receives a signing bonus of $20,000 and earns an annual amount of $50,000, paid at the end of each year for three years, provided that the player has competed in all the specified tournaments for each year. If the player wins a major tournament, she receives a bonus of 20% of the prize money won at the tournament. In return, the player is required to wear advertising logos on tennis apparel, play a specified number of tournaments and attend photo/film sessions for advertising purposes. The different payments are not interrelated. (5 marks)
(c) Minco leased its head office during the current accounting period and the agreement terminates in six years’ time. There is a clause in the operating lease relating to the internal condition of the property at the termination of the lease. The clause states that the internal condition of the property should be identical to that at the outset of the lease. Minco has improved the building by adding another floor to part of the building during the current accounting period. There is also a clause which enables the landlord to recharge Minco for costs relating to the general disrepair of the building at the end of the lease. In addition, the landlord can recharge any costs of repairing the roof immediately. The landlord intends to replace part of the roof of the building during the current period. (5 marks)
(d) Minco acquired a property for $4 million and annual depreciation of $300,000 is charged on the straight line basis. At the end of the previous financial year of 31 May 2013, when accumulated depreciation was $1 million, a further amount relating to an impairment loss of $350,000 was recognised, which resulted in the property being valued at its estimated value in use. On 1 October 2013, as a consequence of a proposed move to new premises, the property was classified as held for sale. At the time of classification as held for sale, the fair value less costs to sell was $2·4 million. At the date of the published interim financial statements, 1 December 2013, the property market had improved and the fair value less costs to sell was reassessed at $2·52 million and at the year end on 31 May 2014 it had improved even further, so that the fair value less costs to sell was $2·95 million. The property was sold on 5 June 2014 for $3 million. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above items should be dealt with in the financial statements of Minco.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the four issues above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 3 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
第2题
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
Aspire, a public limited company, operates many of its activities overseas. The directors have asked for advice on the correct accounting treatment of several aspects of Aspire’s overseas operations. Aspire’s functional currency is the dollar.
(a) Aspire has created a new subsidiary, which is incorporated in the same country as Aspire. The subsidiary has issued 2 million dinars of equity capital to Aspire, which paid for these shares in dinars. The subsidiary has also raised 100,000 dinars of equity capital from external sources and has deposited the whole of the capital with a bank in an overseas country whose currency is the dinar. The capital is to be invested in dinar denominated bonds. The subsidiary has a small number of staff and its operating expenses, which are low, are incurred in dollars. The profits are under the control of Aspire. Any income from the investment is either passed on to Aspire in the form. of a dividend or reinvested under instruction from Aspire. The subsidiary does not make any decisions as to where to place the investments.
Aspire would like advice on how to determine the functional currency of the subsidiary. (7 marks)
(b) Aspire has a foreign branch which has the same functional currency as Aspire. The branch’s taxable profits are determined in dinars. On 1 May 2013, the branch acquired a property for 6 million dinars. The property had an expected useful life of 12 years with a zero residual value. The asset is written off for tax purposes over eight years. The tax rate in Aspire’s jurisdiction is 30% and in the branch’s jurisdiction is 20%. The foreign branch uses the cost model for valuing its property and measures the tax base at the exchange rate at the reporting date.
Aspire would like an explanation (including a calculation) as to why a deferred tax charge relating to the asset arises in the group financial statements for the year ended 30 April 2014 and the impact on the financial statements if the tax base had been translated at the historical rate. (6 marks)
(c) On 1 May 2013, Aspire purchased 70% of a multi-national group whose functional currency was the dinar. The purchase consideration was $200 million. At acquisition, the net assets at cost were 1,000 million dinars. The fair values of the net assets were 1,100 million dinars and the fair value of the non-controlling interest was 250 million dinars.
Aspire uses the full goodwill method. Aspire wishes to know how to deal with goodwill arising on the above acquisition in the group financial statements for the year ended 30 April 2014. (5 marks)
(d) Aspire took out a foreign currency loan of 5 million dinars at a fixed interest rate of 8% on 1 May 2013. The interest is paid at the end of each year. The loan will be repaid after two years on 30 April 2015. The interest rate is the current market rate for similar two-year fixed interest loans.
Aspire requires advice on how to account for the loan and interest in the financial statements for the year ended 30 April 2014. (5 marks)
Aspire has a financial statement year end of 30 April 2014 and the average currency exchange rate for the year is not materially different from the actual rate.

Required:
Advise the directors of Aspire on their various requests above, showing suitable calculations where necessary.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the four issues above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 2 for clarity and quality of presentation. (2 marks)
第3题
Section A – THIS ONE question is compulsory and MUST be attempted
The following draft financial statements relate to Marchant, a public limited company.
Marchant Group: Draft statements of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the year ended 30 April 2014.
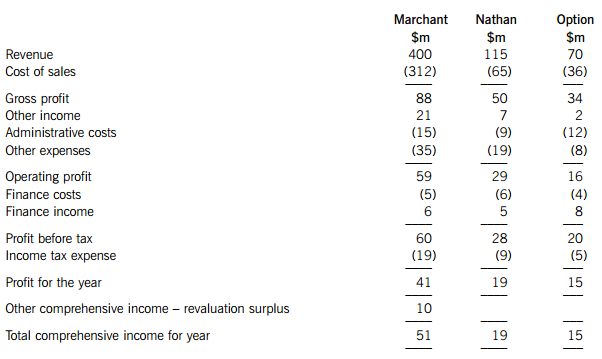
The following information is relevant to the preparation of the group statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income:
1. On 1 May 2012, Marchant acquired 60% of the equity interests of Nathan, a public limited company. The purchase consideration comprised cash of $80 million and the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired was $110 million at that date. The fair value of the non-controlling interest (NCI) in Nathan was $45 million on 1 May 2012. Marchant wishes to use the ‘full goodwill’ method for all acquisitions. The share capital and retained earnings of Nathan were $25 million and $65 million respectively and other components of equity were $6 million at the date of acquisition. The excess of the fair value of the identifiable net assets at acquisition is due to non-depreciable land.
Goodwill has been impairment tested annually and as at 30 April 2013 had reduced in value by 20%. However at 30 April 2014, the impairment of goodwill had reversed and goodwill was valued at $2 million above its original value. This upward change in value has already been included in above draft financial statements of Marchant prior to the preparation of the group accounts.
2. Marchant disposed of an 8% equity interest in Nathan on 30 April 2014 for a cash consideration of $18 million and had accounted for the gain or loss in other income. The carrying value of the net assets of Nathan at 30 April 2014 was $120 million before any adjustments on consolidation. Marchant accounts for investments in subsidiaries using IFRS 9 Financial Instruments and has made an election to show gains and losses in other comprehensive income. The carrying value of the investment in Nathan was $90 million at 30 April 2013 and $95 million at 30 April 2014 before the disposal of the equity interest.
3. Marchant acquired 60% of the equity interests of Option, a public limited company, on 30 April 2012. The purchase consideration was cash of $70 million. Option’s identifiable net assets were fair valued at $86 million and the NCI had a fair value of $28 million at that date. On 1 November 2013, Marchant disposed of a 40% equity interest in Option for a consideration of $50 million. Option’s identifiable net assets were $90 million and the value of the NCI was $34 million at the date of disposal. The remaining equity interest was fair valued at $40 million. After the disposal, Marchant exerts significant influence. Any increase in net assets since acquisition has been reported in profit or loss and the carrying value of the investment in Option had not changed since acquisition. Goodwill had been impairment tested and no impairment was required. No entries had been made in the financial statements of Marchant for this transaction other than for cash received.
4. Marchant sold inventory to Nathan for $12 million at fair value. Marchant made a loss on the transaction of $2 million and Nathan still holds $8 million in inventory at the year end.
5. The following information relates to Marchant’s pension scheme:
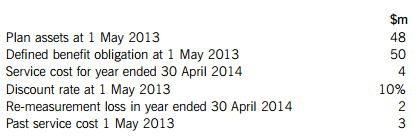
The pension costs have not been accounted for in total comprehensive income.
6. On 1 May 2012, Marchant purchased an item of property, plant and equipment for $12 million and this is being depreciated using the straight line basis over 10 years with a zero residual value. At 30 April 2013, the asset was revalued to $13 million but at 30 April 2014, the value of the asset had fallen to $7 million. Marchant uses the revaluation model to value its non-current assets. The effect of the revaluation at 30 April 2014 had not been taken into account in total comprehensive income but depreciation for the year had been charged.
7. On 1 May 2012, Marchant made an award of 8,000 share options to each of its seven directors. The condition attached to the award is that the directors must remain employed by Marchant for three years. The fair value of each option at the grant date was $100 and the fair value of each option at 30 April 2014 was $110. At 30 April 2013, it was estimated that three directors would leave before the end of three years. Due to an economic downturn, the estimate of directors who were going to leave was revised to one director at 30 April 2014. The expense for the year as regards the share options had not been included in profit or loss for the current year and no directors had left by 30 April 2014.
8. A loss on an effective cash flow hedge of Nathan of $3 million has been included in the subsidiary’s finance costs.
9. Ignore the taxation effects of the above adjustments unless specified. Any expense adjustments should be amended in other expenses.
Required:
(a) (i) Prepare a consolidated statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the year ended 30 April 2014 for the Marchant Group. (30 marks)
(ii) Explain, with suitable calculations, how the sale of the 8% interest in Nathan should be dealt with in the group statement of financial position at 30 April 2014. (5 marks)
(b) The directors of Marchant have strong views on the usefulness of the financial statements after their move to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs). They feel that IFRSs implement a fair value model. Nevertheless, they are of the opinion that IFRSs are failing users of financial statements as they do not reflect the financial value of an entity.
Required:
Discuss the directors’ views above as regards the use of fair value in IFRSs and the fact that IFRSs do not reflect the financial value of an entity. (9 marks)
(c) Marchant plans to update its production process and the directors feel that technology-led production is the only feasible way in which the company can remain competitive. Marchant operates from a leased property and the leasing arrangement was established in order to maximise taxation benefits. However, the financial statements have not shown a lease asset or liability to date.
A new financial controller joined Marchant just after the financial year end of 30 April 2014 and is presently reviewing the financial statements to prepare for the upcoming audit and to begin making a loan application to finance the new technology. The financial controller feels that the lease relating to both the land and buildings should be treated as a finance lease but the finance director disagrees. The finance director does not wish to recognise the lease in the statement of financial position and therefore wishes to continue to treat it as an operating lease. The finance director feels that the lease does not meet the criteria for a finance lease, and it was made clear by the finance director that showing the lease as a finance lease could jeopardise the loan application.
Required:
Discuss the ethical and professional issues which face the financial controller in the above situation. (6 marks)
第4题
th the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) on fair value measurement by issuing IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement. IFRS 13 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and requires significant disclosures relating to fair value measurement.
The IASB wanted to enhance the guidance available for assessing fair value in order that users could better gauge the valuation techniques and inputs used to measure fair value. There are no new requirements as to when fair value accounting is required, but the IFRS gives guidance regarding fair value measurements in existing standards. Fair value measurements are categorised into a three-level hierarchy, based on the type of inputs to the valuation techniques used. However, the guidance in IFRS 13 does not apply to transactions dealt with by certain specific standards.
Required:
(i) Discuss the main principles of fair value measurement as set out in IFRS 13. (7 marks)
(ii) Describe the three-level hierarchy for fair value measurements used in IFRS 13. (6 marks)
(b) Jayach, a public limited company, is reviewing the fair valuation of certain assets and liabilities in light of the introduction of IFRS 13.
It carries an asset that is traded in different markets and is uncertain as to which valuation to use. The asset has to be valued at fair value under International Financial Reporting Standards. Jayach currently only buys and sells the asset in the Australasian market. The data relating to the asset are set out below:
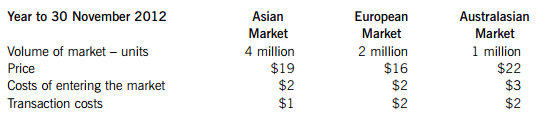
Additionally, Jayach had acquired an entity on 30 November 2012 and is required to fair value a decommissioning liability. The entity has to decommission a mine at the end of its useful life, which is in three years’ time. Jayach has determined that it will use a valuation technique to measure the fair value of the liability. If Jayach were allowed to transfer the liability to another market participant, then the following data would be used.

Jayach needs advice on how to fair value the liability.
Required:
Discuss, with relevant computations, how Jayach should fair value the above asset and liability under IFRS 13. (10 marks)
Professional marks will be awarded in question 4 for the clarity and quality of the presentation and discussion. (2 marks)
第5题
International Financial Reporting Standards.
(a) Blackcutt wishes to create a credible investment property portfolio with a view to determining if any property may be considered surplus to the functional objectives and requirements of the local government organisation. The following portfolio of property is owned by Blackcutt.
Blackcutt owns several plots of land. Some of the land is owned by Blackcutt for capital appreciation and this may be sold at any time in the future. Other plots of land have no current purpose as Blackcutt has not determined whether it will use the land to provide services such as those provided by national parks or for short-term sale in the ordinary course of operations.
The local government organisation supplements its income by buying and selling property. The housing department regularly sells part of its housing inventory in the ordinary course of its operations as a result of changing demographics. Part of the inventory, which is not held for sale, is to provide housing to low-income employees at below market rental. The rent paid by employees covers the cost of maintenance of the property. (7 marks)
(b) Blackcutt has outsourced its waste collection to a private sector provider called Waste and Co and pays an annual amount to Waste and Co for its services. Waste and Co purchases the vehicles and uses them exclusively for Blackcutt’s waste collection. The vehicles are painted with the Blackcutt local government organisation name and colours. Blackcutt can use the vehicles and the vehicles are used for waste collection for nearly all of the asset’s life. In the event of Waste and Co’s business ceasing, Blackcutt can obtain legal title to the vehicles and carry on the waste collection service. (6 marks)
(c) Blackcutt owns a warehouse. Chemco has leased the warehouse from Blackcutt and is using it as a storage facility for chemicals. The national government has announced its intention to enact environmental legislation requiring property owners to accept liability for environmental pollution. As a result, Blackcutt has introduced a hazardous chemical policy and has begun to apply the policy to its properties. Blackcutt has had a report that the chemicals have contaminated the land surrounding the warehouse. Blackcutt has no recourse against Chemco or its insurance company for the clean-up costs of the pollution. At 30 November 2012, it is virtually certain that draft legislation requiring a clean up of land already contaminated will be enacted shortly after the year end. (4 marks)
(d) On 1 December 2006, Blackcutt opened a school at a cost of $5 million. The estimated useful life of the school was 25 years. On 30 November 2012, the school was closed because numbers using the school declined unexpectedly due to a population shift caused by the closure of a major employer in the area. The school is to be converted for use as a library, and there is no expectation that numbers using the school will increase in the future and thus the building will not be reopened for use as a school. The current replacement cost for a library of equivalent size to the school is $2·1 million. Because of the nature of the non-current asset, value-in-use and net selling price are unrealistic estimates of the value of the school. The change in use would have no effect on the estimated life of the building. (6 marks)
Required:
Discuss how the above events should be accounted for in the financial statements of Blackcutt.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the four events above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 3 for the clarity and quality of the presentation and discussion. (2 marks)
第6题
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
(a) Coate, a public limited company, is a producer of ecologically friendly electrical power (green electricity). Coate’s revenue comprises mainly the sale of electricity and green certificates. Coate obtains green certificates under a national government scheme. Green certificates represent the environmental value of green electricity. The national government requires suppliers who do not produce green electricity to purchase a certain number of green certificates. Suppliers who do not produce green electricity can buy green certificates either on the market on which they are traded or directly from a producer such as Coate. The national government wishes to give incentives to producers such as Coate by allowing them to gain extra income in this way.
Coate obtains the certificates from the national government on satisfactory completion of an audit by an independent organisation, which confirms the origin of production. Coate then receives a certain number of green certificates from the national government depending on the volume of green electricity generated. The green certificates are allocated to Coate on a quarterly basis by the national government and Coate can trade the green certificates.
Coate is uncertain as to the accounting treatment of the green certificates in its financial statements for the period ended 30 November 2012 and how to treat the green certificates which were not sold at the end of the reporting period. (7 marks)
(b) During the year ended 30 November 2012, Coate acquired an overseas subsidiary whose financial statements are prepared in a different currency to Coate. The amounts reported in the consolidated statement of cash flows included the effect of changes in foreign exchange rates arising on the retranslation of its overseas operations. Additionally, the group’s consolidated statement of cash flows reported as a loss the effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents as Coate held some foreign currency of its own denominated in cash. (5 marks)
Under the shareholder agreement, consensus is required with respect to:
– significant changes in the company’s activities;
– plans or budgets that deviate from the business plan;
– accounting policies; acquisition of assets above a certain value; employment or dismissal of senior employees; distribution of dividends or establishment of loan facilities
Coate feels that the consensus required above does not constitute a hindrance to the power to control Patten, as it is customary within the industry to require shareholder consensus for decisions of the types listed in the shareholders’ agreement.
(d) In the notes to Coate’s financial statements for the year ended 30 November 2012, the tax expense included an amount in respect of ‘Adjustments to current tax in respect of prior years’ and this expense had been treated as a prior year adjustment. These items related to adjustments arising from tax audits by the authorities in relation to previous reporting periods.
The issues that resulted in the tax audit adjustment were not a breach of tax law but related predominantly to transfer pricing issues, for which there was a range of possible outcomes that were negotiated during 2012 with the taxation authorities. Further at 30 November 2011, Coate had accounted for all known issues arising from the audits to that date and the tax adjustment could not have been foreseen as at 30 November 2011, as the audit authorities changed the scope of the audit. No penalties were expected to be applied by the taxation authorities.
Required:
Discuss how the above events should be accounted for in the individual or, as appropriate, the consolidated financial statements of Coate.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the four events above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 2 for the clarity and quality of the presentation and discussion. (2 marks)
第7题
Section A – THIS ONE question is compulsory and MUST be attempted
Minny is a company which operates in the service sector. Minny has business relationships with Bower and Heeny. All three entities are public limited companies. The draft statements of financial position of these entities are as follows at 30 November 2012:
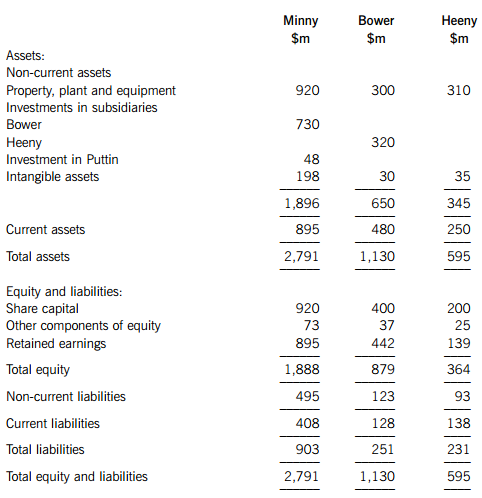
The following information is relevant to the preparation of the group financial statements:
1. On 1 December 2010, Minny acquired 70% of the equity interests of Bower. The purchase consideration comprised cash of $730 million. At acquisition, the fair value of the non-controlling interest in Bower was $295 million. On 1 December 2010, the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired was $835 million and retained earnings of Bower were $319 million and other components of equity were $27 million. The excess in fair value is due to non-depreciable land.
2. On 1 December 2011, Bower acquired 80% of the equity interests of Heeny for a cash consideration of $320 million. The fair value of a 20% holding of the non-controlling interest was $72 million; a 30% holding was $108 million and a 44% holding was $161 million. At the date of acquisition, the identifiable net assets of Heeny had a fair value of $362 million, retained earnings were $106 million and other components of equity were $20 million. The excess in fair value is due to non-depreciable land.
It is the group’s policy to measure the non-controlling interest at fair value at the date of acquisition.
3. Both Bower and Heeny were impairment tested at 30 November 2012. The recoverable amounts of both cash generating units as stated in the individual financial statements at 30 November 2012 were Bower, $1,425 million, and Heeny, $604 million, respectively. The directors of Minny felt that any impairment of assets was due to the poor performance of the intangible assets. The recoverable amount has been determined without consideration of liabilities which all relate to the financing of operations.
4. Minny acquired a 14% interest in Puttin, a public limited company, on 1 December 2010 for a cash consideration of $18 million. The investment was accounted for under IFRS 9 Financial Instruments and was designated as at fair value through other comprehensive income. On 1 June 2012, Minny acquired an additional 16% interest in Puttin for a cash consideration of $27 million and achieved significant influence. The value of the original 14% investment on 1 June 2012 was $21 million. Puttin made profits after tax of $20 million and $30 million for the years to 30 November 2011 and 30 November 2012 respectively. On 30 November 2012, Minny received a dividend from Puttin of $2 million, which has been credited to other components of equity
5. Minny purchased patents of $10 million to use in a project to develop new products on 1 December 2011. Minny has completed the investigative phase of the project, incurring an additional cost of $7 million and has determined that the product can be developed profitably. An effective and working prototype was created at a cost of $4 million and in order to put the product into a condition for sale, a further $3 million was spent. Finally, marketing costs of $2 million were incurred. All of the above costs are included in the intangible assets of Minny.
6. Minny intends to dispose of a major line of the parent’s business operations. At the date the held for sale criteria were met, the carrying amount of the assets and liabilities comprising the line of business were:

It is anticipated that Minny will realise $30 million for the business. No adjustments have been made in the financial statements in relation to the above decision.
Required:
(a) Prepare the consolidated statement of financial position for the Minny Group as at 30 November 2012. (35 marks)
(b) Minny intends to dispose of a major line of business in the above scenario and the entity has stated that the held for sale criteria were met under IFRS 5 Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations. The criteria in IFRS 5 are very strict and regulators have been known to question entities on the application of the standard. The two criteria which must be met before an asset or disposal group will be defined as recovered principally through sale are: that it must be available for immediate sale in its present condition and the sale must be highly probable.
Required:
Discuss what is meant in IFRS 5 by ‘available for immediate sale in its present condition’ and ‘the sale must be highly probable’, setting out briefly why regulators may question entities on the application of the standard. (7 marks)
(c) Bower has a property which has a carrying value of $2 million at 30 November 2012. This property had been revalued at the year end and a revaluation surplus of $400,000 had been recorded in other components of equity. The directors were intending to sell the property to Minny for $1 million shortly after the year end. Bower previously used the historical cost basis for valuing property.
Required: Without adjusting your answer to part (a), discuss the ethical and accounting implications of the above intended sale of assets to Minny by Bower. (8 marks)
第8题
es and Contingent Assets, has been in place for many years and is sufficiently well understood and consistently applied in most areas. The IASB feels it is time for a fundamental change in the underlying principles for the recognition and measurement of non-financial liabilities. To this end, the Board has issued an Exposure Draft, ‘Measurement of Liabilities in IAS 37 – Proposed amendments to IAS 37’.
Required:
(i) Discuss the existing guidance in IAS 37 as regards the recognition and measurement of provisions and why the IASB feels the need to replace this guidance; (9 marks)
(ii) Describe the new proposals that the IASB has outlined in the Exposure Draft. (7 marks)
(b) Royan, a public limited company, extracts oil and has a present obligation to dismantle an oil platform. at the end of the platform’s life, which is 10 years. Royan cannot cancel this obligation or transfer it. Royan intends to carry out the dismantling work itself and estimates the cost of the work to be $150 million in 10 years time. The present value of the work is $105 million.
A market exists for the dismantling of an oil platform. and Royan could hire a third party contractor to carry out the work. The entity feels that if no risk or probability adjustment were needed then the cost of the external contractor would be $180 million in ten years time. The present value of this cost is $129 million. If risk and probability are taken into account, then there is a probability of 40% that the present value will be $129 million and 60% probability that it would be $140 million, and there is a risk that the costs may increase by $5 million.
Required:
Describe the accounting treatment of the above events under IAS 37 and the possible outcomes under the proposed amendments in the Exposure Draft. (7 marks)
Professional marks will be awarded in question 4 for the quality of the discussion. (2 marks)
第9题
Ethan, a public limited company, develops, operates and sells investment properties.
(a) Ethan focuses mainly on acquiring properties where it foresees growth potential, through rental income as well as value appreciation. The acquisition of an investment property is usually realised through the acquisition of the entity, which holds the property.
In Ethan’s consolidated financial statements, investment properties acquired through business combinations are recognised at fair value, using a discounted cash flow model as approximation to fair value. There is currently an active market for this type of property. The difference between the fair value of the investment property as determined under the accounting policy, and the value of the investment property for tax purposes results in a deferred tax liability.
Goodwill arising on business combinations is determined using the measurement principles for the investment properties as outlined above. Goodwill is only considered impaired if and when the deferred tax liability is reduced below the amount at which it was first recognised. This reduction can be caused both by a reduction in the value of the real estate or a change in local tax regulations. As long as the deferred tax liability is equal to, or larger than, the prior year, no impairment is charged to goodwill. Ethan explained its accounting treatment by confirming that almost all of its goodwill is due to the deferred tax liability and that it is normal in the industry to account for goodwill in this way.
Since 2008, Ethan has incurred substantial annual losses except for the year ended 31 May 2011, when it made a small profit before tax. In year ended 31 May 2011, most of the profit consisted of income recognised on revaluation of investment properties. Ethan had announced early in its financial year ended 31 May 2012 that it anticipated substantial growth and profit. Later in the year, however, Ethan announced that the expected profit would not be achieved and that, instead, a substantial loss would be incurred. Ethan had a history of reporting considerable negative variances from its budgeted results. Ethan’s recognised deferred tax assets have been increasing year-on-year despite the deferred tax liabilities recognised on business combinations. Ethan’s deferred tax assets consist primarily of unused tax losses that can be carried forward which are unlikely to be offset against anticipated future taxable profits. (11 marks)
(b) Ethan wishes to apply the fair value option rules of IFRS 9 Financial Instruments to debt issued to finance its investment properties. Ethan’s argument for applying the fair value option is based upon the fact that the recognition of gains and losses on its investment properties and the related debt would otherwise be inconsistent. Ethan argued that there is a specific financial correlation between the factors, such as interest rates, that form. the basis for determining the fair value of both Ethan’s investment properties and the related debt. (7 marks)
(c) Ethan has an operating subsidiary, which has in issue A and B shares, both of which have voting rights. Ethan holds 70% of the A and B shares and the remainder are held by shareholders external to the group. The subsidiary is obliged to pay an annual dividend of 5% on the B shares. The dividend payment is cumulative even if the subsidiary does not have sufficient legally distributable profit at the time the payment is due.
In Ethan’s consolidated statement of financial position, the B shares of the subsidiary were accounted for in the same way as equity instruments would be, with the B shares owned by external parties reported as a non-controlling interest. (5 marks)
Required: Discuss how the above transactions and events should be recorded in the consolidated financial statements of Ethan. Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the three transactions above. Professional marks will be awarded in question 3 for the quality of the discussion. (2 marks)
第10题
Section B – TWO questions ONLY to be attempted
William is a public limited company and would like advice in relation to the following transactions.
(a) William owned a building on which it raised finance. William sold the building for $5 million to a finance company on 1 June 2011 when the carrying amount was $3·5 million. The same building was leased back from the finance company for a period of 20 years, which was felt to be equivalent to the majority of the asset’s economic life. The lease rentals for the period are $441,000 payable annually in arrears. The interest rate implicit in the lease is 7%. The present value of the minimum lease payments is the same as the sale proceeds.
William wishes to know how to account for the above transaction for the year ended 31 May 2012. (7 marks)
(b) William operates a defined benefit scheme for its employees. At June 2011, the net pension liability recognised in the statement of financial position was $18 million, excluding an unrecognised actuarial gain of $15 million which William wishes to spread over the remaining working lives of the employees. The scheme was revised on 1 June 2011. This resulted in the benefits being enhanced for some members of the plan and because benefits do not vest for these members for five years, William wishes to spread the increased cost over that period. However, part of the scheme was to be closed, without any redundancy of employees.
William requires advice on how to account for the above scheme under IAS 19 Employee Benefits including the presentation and measurement of the pension expense. (7 marks)
(c) On 1 June 2009, William granted 500 share appreciation rights to each of its 20 managers. All of the rights vest after two years service and they can be exercised during the following two years up to 31 May 2013. The fair value of the right at the grant date was $20. It was thought that three managers would leave over the initial two-year period and they did so. The fair value of each right was as follows:

On 31 May 2012, seven managers exercised their rights when the intrinsic value of the right was $21.
William wishes to know what the liability and expense will be at 31 May 2012. (5 marks)
(d) William acquired another entity, Chrissy, on 1 May 2012. At the time of the acquisition, Chrissy was being sued as there is an alleged mis-selling case potentially implicating the entity. The claimants are suing for damages of $10 million. William estimates that the fair value of any contingent liability is $4 million and feels that it is more likely than not that no outflow of funds will occur.
William wishes to know how to account for this potential liability in Chrissy’s entity financial statements and whether the treatment would be the same in the consolidated financial statements. (4 marks)
Required: Discuss, with suitable computations, the advice that should be given to William in accounting for the above events.
Note: The mark allocation is shown against each of the four events above.
Professional marks will be awarded in question 2 for the quality of the discussion. (2 marks)
 警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
为了保护您的账号安全,请在“上学吧”公众号进行验证,点击“官网服务”-“账号验证”后输入验证码“”完成验证,验证成功后方可继续查看答案!
