 重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
重要提示:
请勿将账号共享给其他人使用,违者账号将被封禁!
 题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
It currently produces and sells 80,000 units per annum, with production of them being restricted by the short supply of labour. Each control panel includes two main components – one key pad and one display screen. At present, Robber Co manufactures both of these components in-house. However, the company is currently considering outsourcing the production of keypads and/or display screens. A newly established company based in Burgistan is keen to secure a place in the market, and has offered to supply the keypads for the equivalent of $4·10 per unit and the display screens for the equivalent of $4·30 per unit. This price has been guaranteed for two years.
The current total annual costs of producing the keypads and the display screens are:
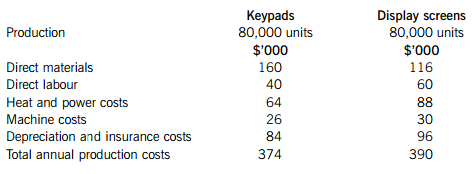
Notes:
1. Materials costs for keypads are expected to increase by 5% in six months’ time; materials costs for display screens are only expected to increase by 2%, but with immediate effect.
2. Direct labour costs are purely variable and not expected to change over the next year.
3. Heat and power costs include an apportionment of the general factory overhead for heat and power as well as the costs of heat and power directly used for the production of keypads and display screens. The general apportionment included is calculated using 50% of the direct labour cost for each component and would be incurred irrespective of whether the components are manufactured in-house or not.
4. Machine costs are semi-variable; the variable element relates to set up costs, which are based upon the number of batches made. The keypads’ machine has fixed costs of $4,000 per annum and the display screens’ machine has fixed costs of $6,000 per annum. Whilst both components are currently made in batches of 500, this would need to change, with immediate effect, to batches of 400.
5. 60% of depreciation and insurance costs relate to an apportionment of the general factory depreciation and insurance costs; the remaining 40% is specific to the manufacture of keypads and display screens.
Required:
(a) Advise Robber Co whether it should continue to manufacture the keypads and display screens in-house or whether it should outsource their manufacture to the supplier in Burgistan, assuming it continues to adopt a policy to limit manufacture and sales to 80,000 control panels in the coming year. (8 marks)
(b) Robber Co takes 0·5 labour hours to produce a keypad and 0·75 labour hours to produce a display screen. Labour hours are restricted to 100,000 hours and labour is paid at $1 per hour. Robber Co wishes to increase its supply to 100,000 control panels (i.e. 100,000 each of keypads and display screens). Advise Robber Co as to how many units of keypads and display panels they should either manufacture and/or outsource in order to minimise their costs. (7 marks)
(c) Discuss the non-financial factors that Robber Co should consider when making a decision about outsourcing the manufacture of keypads and display screens. (5 marks)
 更多“Robber Co manufactures control panels for burglar alarms, a very profitable product. Every”相关的问题
更多“Robber Co manufactures control panels for burglar alarms, a very profitable product. Every”相关的问题
第1题
of them is called ‘Ooze’ and contains three types of sweeteners: honey, sugar and syrup. The standard materials usage and cost for one unit of ‘Ooze’ (one packet) is as follows:
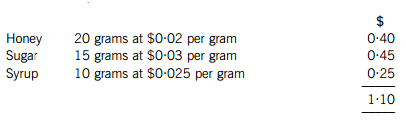
In the three months ended 30 November 2011, Choc Co produced 101,000 units of ‘Ooze’ using 2,200 kg of honey, 1,400 kg of sugar and 1,050 kg of syrup. Note: there are 1,000 grams in a kilogram (kg).
Choc Co has used activity-based costing to allocate its overheads for a number of years. One of its main overheads is machine set-up costs. In the three months ended 30 November 2011, the following information was available in relation to set-up costs:

Required:
(a) Calculate the following variances for materials in Ooze:
(i) Total materials usage variance; (4 marks)
(ii) Total materials mix variance; (4 marks)
(iii) Total materials quantity (yield) variance. (4 marks)
(b) Calculate the following activity-based variances in relation to the set-up cost of the machines:
(i) The expenditure variance; (3 marks)
(ii) The efficiency variance. (3 marks)
(c) Briefly outline the steps involved in allocating overheads using activity based costing. (2 marks)
第2题
Fit Co specialises in the manufacture of a small range of hi-tech products for the fitness market. They are currently considering the development of a new type of fitness monitor, which would be the first of its kind in the market. It would take one year to develop, with sales then commencing at the beginning of the second year. The product is expected to have a life cycle of two years, before it is replaced with a technologically superior product. The following cost estimates have been made.

Note: You should ignore the time value of money.
Required:
(a) Calculate the life cycle cost per unit. (6 marks)
(b) After preparing the cost estimates above, the company realises that it has not taken into account the effect of the learning curve on the production process. The variable manufacturing cost per unit above, of $40 in year 2 and $42 in year 3, includes a cost for 0·5 hours of labour. The remainder of the variable manufacturing cost is not driven by labour hours. The year 2 cost per hour for labour is $24 and the year 3 cost is $26 per hour. Subsequently, it has now been estimated that, although the first unit is expected to take 0·5 hours, a learning curve of 95% is expected to occur until the 100th unit has been completed.
Calculate the revised life cycle cost per unit, taking into account the effect of the learning curve.
Note: the value of the learning co-efficient, b, is –0·0740005. (10 marks)
(c) Discuss the benefits of life cycle costing. (4 marks)
第3题
PC Co. When you meet the production manager, you overhear him speaking to one of his staff, saying:
‘Budgeting is a waste of time. I don’t see the point of it. It tells us what we can’t afford but it doesn’t keep us from buying it. It simply makes us invent new ways of manipulating figures. If all levels of management aren’t involved in the setting of the budget, they might as well not bother preparing one.’
Required:
(a) Identify and explain SIX objectives of a budgetary control system. (9 marks)
(b) Discuss the concept of a participative style. of budgeting in terms of the six objectives identified in part (a). (11 marks)
第4题
of a main unit plus a set of bath fittings. The company is split into two divisions, A and B. Division A manufactures the bath and Division B manufactures sets of bath fittings. Currently, all of Division A’s sales are made externally. Division B, however, sells to Division A as well as to external customers. Both of the divisions are profit centres.
The following data is available for both divisions:

The transfer price charged by Division B to Division A was negotiated some years ago between the previous divisional managers, who have now both been replaced by new managers. Head Office only allows Division A to purchase its fittings from Division B, although the new manager of Division A believes that he could obtain fittings of the same quality and appearance for $65 per set, if he was given the autonomy to purchase from outside the company. Division B makes no cost savings from supplying internally to Division A rather than selling externally.
Required:
(a) Under the current transfer pricing system, prepare a profit statement showing the profit for each of the divisions and for Bath Co as a whole. Your sales and costs figures should be split into external sales and inter-divisional transfers, where appropriate. (6 marks)
(b) Head Office is considering changing the transfer pricing policy to ensure maximisation of company profits without demotivating either of the divisional managers. Division A will be given autonomy to buy from external suppliers and Division B to supply external customers in priority to supplying to Division A.
Calculate the maximum profit that could be earned by Bath Co if transfer pricing is optimised. (8 marks)
(c) Discuss the issues of encouraging divisional managers to take decisions in the interests of the company as a whole, where transfer pricing is used. Provide a reasoned recommendation of a policy Bath Co should adopt. (6 marks)
第5题
r commercial clients. There are two parts to the business:
– installing telephone systems in businesses, either first time installations or replacement installations;
– supporting the telephone systems with annually renewable maintenance contracts.
T Co has been approached by a potential customer, Push Co, who wants to install a telephone system in new offices it is opening. Whilst the job is not a particularly large one, T Co is hopeful of future business in the form. of replacement systems and support contracts for Push Co. T Co is therefore keen to quote a competitive price for the job. The following information should be considered:
1. One of the company’s salesmen has already been to visit Push Co, to give them a demonstration of the new system, together with a complimentary lunch, the costs of which totalled $400.
2. The installation is expected to take one week to complete and would require three engineers, each of whom is paid a monthly salary of $4,000. The engineers have just had their annually renewable contract renewed with T Co. One of the three engineers has spare capacity to complete the work, but the other two would have to be moved from contract X in order to complete this one. Contract X generates a contribution of $5 per engineer hour. There are no other engineers available to continue with Contract X if these two engineers are taken off the job. It would mean that T Co would miss its contractual completion deadline on Contract X by one week. As a result, T Co would have to pay a one-off penalty of $500. Since there is no other work scheduled for their engineers in one week’s time, it will not be a problem for them to complete Contract X at this point.
3. T Co’s technical advisor would also need to dedicate eight hours of his time to the job. He is working at full capacity, so he would have to work overtime in order to do this. He is paid an hourly rate of $40 and is paid for all overtime at a premium of 50% above his usual hourly rate.
4. Two visits would need to be made by the site inspector to approve the completed work. He is an independent contractor who is not employed by T Co, and charges Push Co directly for the work. His cost is $200 for each visit made.
5. T Co’s system trainer would need to spend one day at Push Co delivering training. He is paid a monthly salary of $1,500 but also receives commission of $125 for each day spent delivering training at a client’s site.
6. 120 telephone handsets would need to be supplied to Push Co. The current cost of these is $18·20 each, although T Co already has 80 handsets in inventory. These were bought at a price of $16·80 each. The handsets are the most popular model on the market and frequently requested by T Co’s customers.
7. Push Co would also need a computerised control system called ‘Swipe 2’. The current market price of Swipe 2 is $10,800, although T Co has an older version of the system, ‘Swipe 1’, in inventory, which could be modified at a cost of $4,600. T Co paid $5,400 for Swipe 1 when it ordered it in error two months ago and has no other use for it. The current market price of Swipe 1 is $5,450, although if T Co tried to sell the one they have, it would be deemed to be ‘used’ and therefore only worth $3,000.
8. 1,000 metres of cable would be required to wire up the system. The cable is used frequently by T Co and it has 200 metres in inventory, which cost $1·20 per metre. The current market price for the cable is $1·30 per metre.
9. You should assume that there are four weeks in each month and that the standard working week is 40 hours long.
Required:
(a) Prepare a cost statement, using relevant costing principles, showing the minimum cost that T Co should charge for the contract. Make DETAILED notes showing how each cost has been arrived at and EXPLAINING why each of the costs above has been included or excluded from your cost statement. (14 marks)
(b) Explain the relevant costing principles used in part (a) and explain the implications of the minimum price that has been calculated in relation to the final price agreed with Push Co. (6 marks)
第6题
ciency, the time has come for all public sector organisations to embrace zero-based budgeting. There is no longer a place for incremental budgeting in any organisation, particularly public sector ones, where zero-based budgeting is far more suitable anyway.’
Required:
(a) Discuss the particular difficulties encountered when budgeting in public sector organisations compared with budgeting in private sector organisations, drawing comparisons between the two types of organisations. (5 marks)
(b) Explain the terms ‘incremental budgeting’ and ‘zero-based budgeting’. (4 marks)
(c) State the main stages involved in preparing zero-based budgets. (3 marks)
(d) Discuss the view that ‘there is no longer a place for incremental budgeting in any organisation, particularly public sector ones,’ highlighting any drawbacks of zero-based budgeting that need to be considered. (8 marks)
第7题
now, it has used traditional absorption costing to allocate overheads to its products. The company is now considering an activity based costing system in the hope that it will improve profitability. Information for the three products for the last year is as follows:

The price for raw materials remained constant throughout the year at $1·20 per kg. Similarly, the direct labour cost for the whole workforce was $14·80 per hour. The annual overhead costs were as follows:

Required:
(a) Calculate the full cost per unit for products A, B and C under traditional absorption costing, using direct labour hours as the basis for apportionment. (5 marks)
(b) Calculate the full cost per unit of each product using activity based costing. (9 marks)
(c) Using your calculation from (a) and (b) above, explain how activity based costing may help The Gadget Co improve the profitability of each product. (6 marks)
第8题
s and lotions are sold to a variety of retailers at a price of $23·20 for each jar of face cream and $16·80 for each bottle of body lotion. Each of the products has a variety of ingredients, with the key ones being silk powder, silk amino acids and aloe vera. Six months ago, silk worms were attacked by disease causing a huge reduction in the availability of silk powder and silk amino acids. The Cosmetic Co had to dramatically reduce production and make part of its workforce, which it had trained over a number of years, redundant.
The company now wants to increase production again by ensuring that it uses the limited ingredients available to maximise profits by selling the optimum mix of creams and lotions. Due to the redundancies made earlier in the year, supply of skilled labour is now limited in the short-term to 160 hours (9,600 minutes) per week, although unskilled labour is unlimited. The purchasing manager is confident that they can obtain 5,000 grams of silk powder and 1,600 grams of silk amino acids per week. All other ingredients are unlimited. The following information is available for the two products:

Each jar of cream sold generates a contribution of $9 per unit, whilst each bottle of lotion generates a contribution of $8 per unit. The maximum demand for lotions is 2,000 bottles per week, although demand for creams is unlimited. Fixed costs total $1,800 per week. The company does not keep inventory although if a product is partially complete at the end of one week, its production will be completed in the following week.
Required:
(a) On the graph paper provided, use linear programming to calculate the optimum number of each product that the Cosmetic Co should make per week, assuming that it wishes to maximise contribution. Calculate the total contribution per week for the new production plan. All workings MUST be rounded to 2 decimal places. (14 marks)
(b) Calculate the shadow price for silk powder and the slack for silk amino acids. All workings MUST be rounded to 2 decimal places. (6 marks)
第9题
ncy tuition courses in the private sector. It makes up its accounts to 30 November each year. In the year ending 30 November 2009, it held 60% of market share. However, over the last twelve months, the accountancy tuition market in general has faced a 20% decline in demand for accountancy training leading to smaller class sizes on courses. In 2009 and before, AT Co suffered from an ongoing problem with staff retention, which had a knock-on effect on the quality of service provided to students. Following the completion of developments that have been ongoing for some time, in 2010 the company was able to offer a far-improved service to students. The developments included:
– A new dedicated 24 hour student helpline
– An interactive website providing instant support to students
– A new training programme for staff
– An electronic student enrolment system
– An electronic marking system for the marking of students’ progress tests. The costs of marking electronically were expected to be $4 million less in 2010 than marking on paper. Marking expenditure is always included in cost of sales
Extracts from the management accounts for 2009 and 2010 are shown below:

On 1 December 2009, management asked all ‘freelance lecturers’ to reduce their fees by at least 10% with immediate effect (‘freelance lecturers’ are not employees of the company but are used to teach students when there are not enough of AT Co’s own lecturers to meet tuition needs). All employees were also told that they would not receive a pay rise for at least one year. Total lecture staff costs (including freelance lecturers) were $41·663 million in 2009 and were included in cost of sales, as is always the case. Freelance lecturer costs represented 35% of these total lecture staff costs. In 2010 freelance lecture costs were $12·394 million. No reduction was made to course prices in the year and the mix of trainees studying for the different qualifications remained the same. The same type and number of courses were run in both 2009 and 2010 and the percentage of these courses that was run by freelance lecturers as opposed to employed staff also remained the same.
Due to the nature of the business, non-financial performance indicators are also used to assess performance, as detailed below.
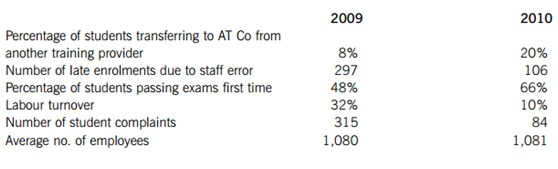
Required:
Assess the performance of the business in 2010 using both financial performance indicators calculated from the above information AND the non-financial performance indicators provided.
NOTE: Clearly state any assumptions and show all workings clearly. Your answer should be structured around the following main headings: turnover; cost of sales; gross profit; indirect expenses; net operating profit. However, in discussing each of these areas you should also refer to the non-financial performance indicators, where relevant.
第10题
s and LCD TVs. It operates within a highly competitive market and is constantly under pressure to reduce prices. Carad Co operates a standard costing system and performs a detailed variance analysis of both products on a monthly basis. Extracts from the management information for the month of November are shown below:

Notes
(1) The budgeted total sales volume for TVs was 1,180 units, consisting of an equal mix of plasma screen TVs and LCD screen TVs. Actual sales volume was 750 plasma TVs and 650 LCD TVs. Standard sales prices are $350 per unit for the plasma TVs and $300 per unit for the LCD TVs. The actual sales prices achieved during November were $330 per unit for plasma TVs and $290 per unit for LCD TVs. The standard contributions for plasma TVs and LCD TVs are $190 and $180 per unit respectively.
(2) The sole reason for this variance was an increase in the purchase price of one of its key components, X. Each plasma TV made and each LCD TV made requires one unit of component X, for which Carad Co’s standard cost is $60 per unit. Due to a shortage of components in the market place, the market price for November went up to $85 per unit for X. Carad Co actually paid $80 per unit for it.
(3) Each plasma TV uses 2 standard hours of labour and each LCD TV uses 1·5 standard hours of labour. The standard cost for labour is $14 per hour and this also reflects the actual cost per labour hour for the company’s permanent staff in November. However, because of the increase in sales and production volumes in November, the company also had to use additional temporary labour at the higher cost of $18 per hour. The total capacity of Carad’s permanent workforce is 2,200 hours production per month, assuming full efficiency. In the month of November, the permanent workforce were wholly efficient, taking exactly 2 hours to complete each plasma TV and exactly 1·5 hours to produce each LCD TV. The total labour variance therefore relates solely to the temporary workers, who took twice as long as the permanent workers to complete their production.
Required:
(a) Calculate the following for the month of November, showing all workings clearly:
(i) The sales price variance and sales volume contribution variance; (6 marks)
(ii) The material price planning variance and material price operational variance; (2 marks)
(iii) The labour rate variance and the labour efficiency variance. (7 marks)
(b) Explain the reasons why Carad Co would be interested in the material price planning variance and the material price operational variance. (5 marks)
 警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
警告:系统检测到您的账号存在安全风险
为了保护您的账号安全,请在“上学吧”公众号进行验证,点击“官网服务”-“账号验证”后输入验证码“”完成验证,验证成功后方可继续查看答案!
